Climate change is the biggest environmental challenge facing society and our business. The effects of climate change, such as global warming and changing weather patterns, could have serious implications for our supply chain - given that our products are mainly agriculture-based - and also for our own operations.
The JT Group supports the Paris Agreement to limit global warming to well below 2℃ and to pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5℃. We are committed to reducing Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions from our business operations and aim to achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions across our entire value chain in the longer term.
The JT Group supports the Paris Agreement to limit global warming to well below 2℃. Our statement on the Paris Agreement can be found here.
Environment and our operations
Tackling climate change

Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
The potential for financial impact associated with climate change is now well known, and concern is growing about its mid- to long-term impact on business operations and financial market stability. We officially endorsed the recommendations of The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in December 2020.
A key aspect of the TCFD recommendations relates to the identification, assessment and management of climate-related risks and their integration into overall risk management.
In line with the expectations of the TCFD, we conducted climate scenario analyses of long-term business risks based on several scenarios.
Governance
Climate-related issues are of strategic importance to our business. Through our business-wide enterprise risk management process, we have identified climate-related risk as one of our enterprise-level risks for our tobacco business, which also needs to be considered in local risk inventories and assessment processes. Board oversight is critical and climate-related issues, especially those that may have impacts on business strategy, are brought up in quarterly Board-level meetings.
Our corporate governance system can be found here.
Strategy
Through climate scenario analysis, we identified two main risks: potential cost increases due to governments raising carbon taxes to further reduce GHG emissions and the impact on tobacco leaf growing due to changes in environmental conditions. Our plan is to mitigate these risks by continuing to implement climate-related initiatives across our value chain and address areas for improvement.
See the JT website for general information on environmental initiatives.
Risk Management
We consider climate-related risks and identify risk mitigation and management approaches through our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) process. We also include these risks in local risk inventories, assessment processes, and action plans, which are partly based on our ongoing country-level climate scenario analysis. We will compare business-wide risks from local assessments and identify the most critical ones.
Metrics and Targets
We have set a target to reduce GHG emissions from our own operations by 47% (2030 versus 2019). We have also set a longer-term GHG emissions reduction target, as well as targets for renewable electricity, backed by our Group-wide climate scenario analysis.
Read more on Environment, Environmental data / External verification / External recognition and Data calculation / Consolidation methods.
Details of Climate Scenario Analysis
We are aiming to achieve net-zero in line with the 1.5℃ target and are examining various risk factors that may have significant financial and strategic implications for our business over short-term (0-5 years), medium-term (5-10 years), and long-term (10-30 years) timeframes. We utilized the IEA NZE2050 climate change scenarios by the International Energy Agency (IEA) for the assessment of transition risks, and scenarios based on typical concentration pathways outlined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), such as Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5) for physical risks.
Please refer to the following for the results of our analysis, which focused on extreme cases of temperature increase.
| Risks and opportu-nities | Applied scenarios and financial impacts (billion yen) | Time frame | Impacts | Countermeasures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃ | 4℃ | Short | Medi-um | Long | |||||
| Transition risks | Measures and policies to address climate-change effect | -8.5 | -2.8 | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
| Carbon pricing | In-house operation | -17.0 | -0.74 | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
| Procurement | -92.0 | -1.9 | |||||||
| Demand/supply shift for materials and energy | -0.9 | 3.3 | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
||
| Physical risks | Changes in farming environments due to rising average temperatures | -3.5 | -34.8 | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
| More frequent, larger-scale abnormal climatic events | -7.1 | -18.8 | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
||
| Tight water supply | -0.1 | -0.1 | ● | ● |
|
|
|||
| Opportunities | Changes in customer lifestyles | 0.1 | 0.7 | ● | ● |
|
|
||
| Effects of rising temperatures on supplier locations and methods | 0.2 | 1.1 | ● | ● |
|
|
|||
Country-level climate scenario analyses
To further understand climate-related issues and potential risks at a more granular level, we have carried out a program of country-level climate scenario analyses in our tobacco business.
From 2020-2022, we completed climate scenario analyses for eleven countries. We prioritized countries where our business includes tobacco leaf sourcing, manufacturing and markets. We used consistent risk modeling and global warming scenarios across all four years.
We assessed potential exposure and vulnerability to climate-related issues for tobacco leaf sourcing, processing, manufacturing and markets using the following indicators: river flooding, sea level rise, heat stress, rainfall variability, water stress, drought, hurricanes, extreme rainfall and frost. We assessed potential exposure using climate modeling based on scientific research and literature, and assessed vulnerability through interviews with local employees. For our analysis, we used three warming projections called Representative Concentration Pathways: RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5.
Emissions reduction / Renewable energy
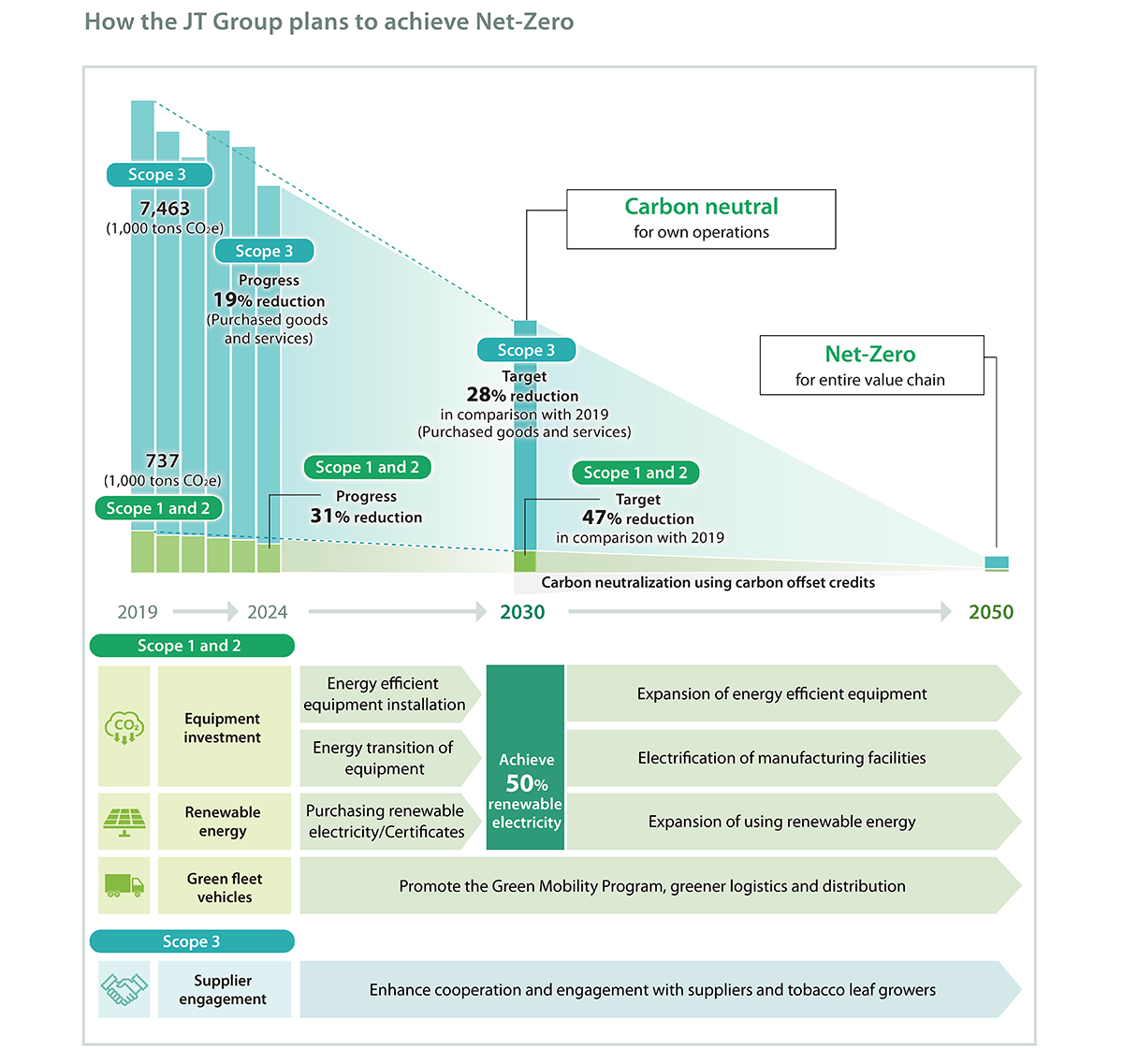
In the JT Group Sustainability Targets, we have set the targets to be Carbon Neutral for its own operations by 2030 and achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions across its entire value chain by 2050.
We have created a roadmap for achieving Net-Zero GHG emissions, and we review our strategies annually. Going forward, the main programs projected to achieve the target relate to further improvements in energy efficiency, renewable energy, and vehicle fuel type and efficiency.
Please see our road map to achieving Net-Zero GHG emissions.
Scope1 and 2 GHG emissions reduction
We commit to reduce absolute Scope1 and 2 GHG emissions by 47% in line with a 1.5 ℃ reduction pathway against a 2019 base year by 2030. As part of our efforts to meet our energy and emissions target, we will increase the proportion of renewable electricity among the forms of energy we use to 50% by 2030, in support of our goal of reaching 100% by 2050. In our tobacco business, we are aiming for 50% by 2025 and 100% by 2040.
To achieve our goals, we will continue introducing renewable energy sources at our operations and investing to raise the ratio of electricity derived from renewables among the forms of energy we use. To accelerate reduction of GHG emissions, we are making use of options available from utility firms to use all or part of the renewable energy they offer, green energy certificates for renewables from third parties, and similar purchasing agreements.
Vehicle emissions are another important consideration for us, and we encourage all of our locations to select alternative, more environmentally friendly fleet vehicles and change the way in which travel is planned, improve the ways in which employees drive or commute, etc. Within our tobacco business, we have launched our Green Mobility Program, designed to reduce emissions associated with our fleet.
Progress toward quantitative targets
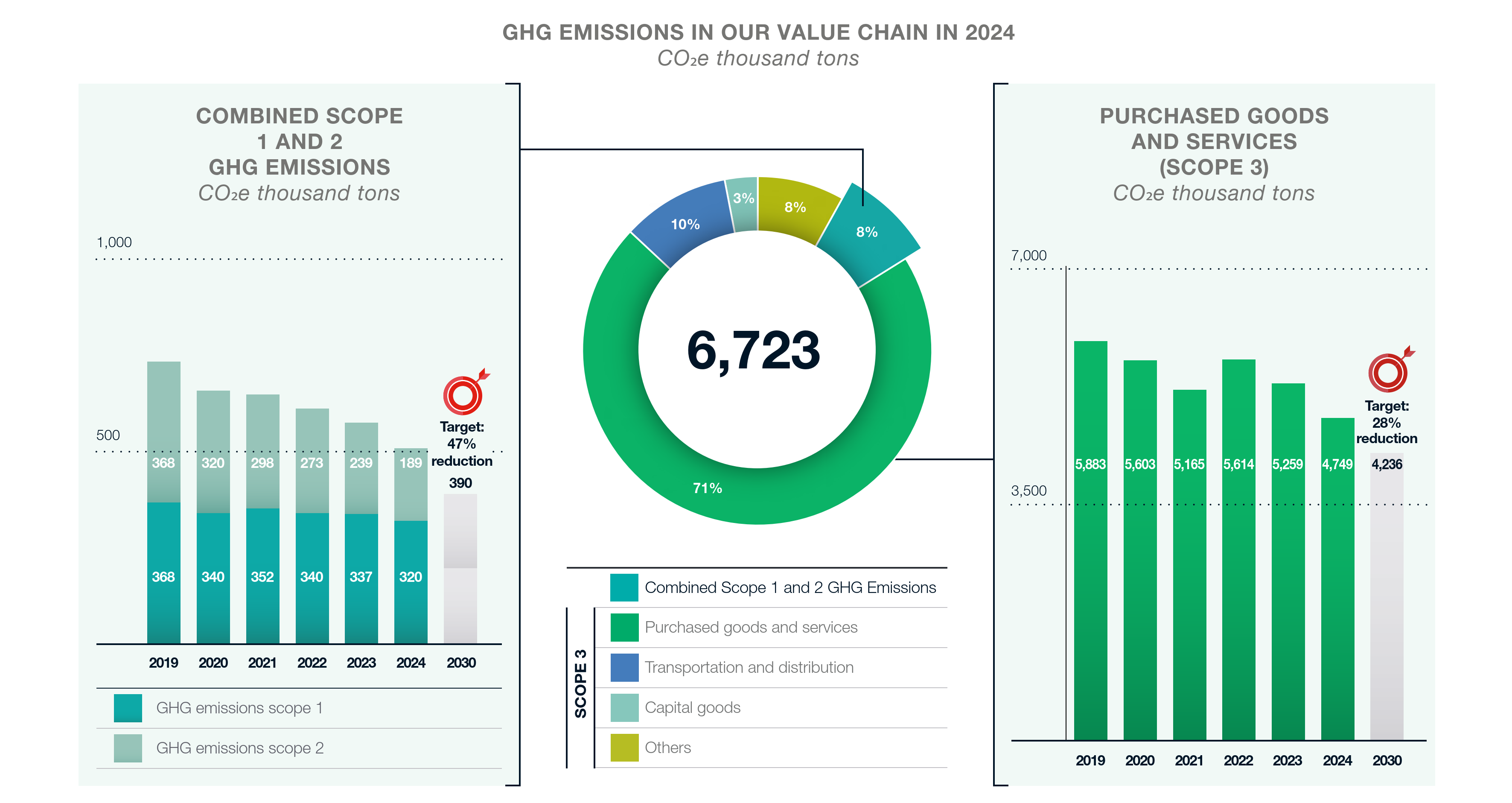
By the end of 2024, we reduced GHG emissions in Scope 1 and 2 by 31% from 2019 by accelerating the introduction of renewable energy.
In addition, 56% of the electricity used in our tobacco business came from renewable sources, accounting for 43% of the electricity used Group-wide in 2024.
Scope3 GHG emissions reduction
As part of the JT Group Sustainability Targets, we are committed to reducing our Scope3 GHG emissions associated with purchased goods and services by 28% by 2030 (compared to 2019).
We believe that initiatives throughout the value chain are important in achieving this target, and we have a long-standing relationship with tobacco growers in Japan. Working closely with tobacco leaf growers and our machinery supplier, we have developed an innovative drying machine which improves fuel efficiency in the tobacco curing process, reducing both the use of non-renewables and GHG emissions. In addition, the new machines help growers to save costs and improve quality, directly impacting our business and improving the environmental impact associated with our tobacco value chain. By the end of 2024, our tobacco leaf growers were using a total of 826 of these drying machines across Japan. We plan to further advance the program by improving the efficiency of the curing system to make the process even more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
We continue focusing our efforts on improving curing efficiency, through barn furnace upgrades and new heat exchange designs. These not only optimize tobacco leaf quality but also reduce wood fuel consumption. In addition, we are addressing the production of wood resources required for tobacco curing through dedicated agroforestry programs and tree-growing initiatives in Tanzania and Zambia, for instance.
Please see other detailed efforts on the JT International sustainability website.
Progress toward quantitative targets
By the end of 2024, we reduced GHG emissions from Scope 3 purchased goods and services by 19% from 2019 by continuously improving leaf tobacco curing efficiency and increasing the use of renewable wood.
GHG emissions in the JT Group: Progress and breakdown of GHG emissions
Science Based Targets
Our GHG emissions reduction target for 2030 has been validated by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), an international initiative on climate change, as 1.5°C aligned. In addition, we have obtained SBTi validation for our target to achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions across the entire value chain by 2050.
